Amphibious AI-Powered Dredger Developed in Russia
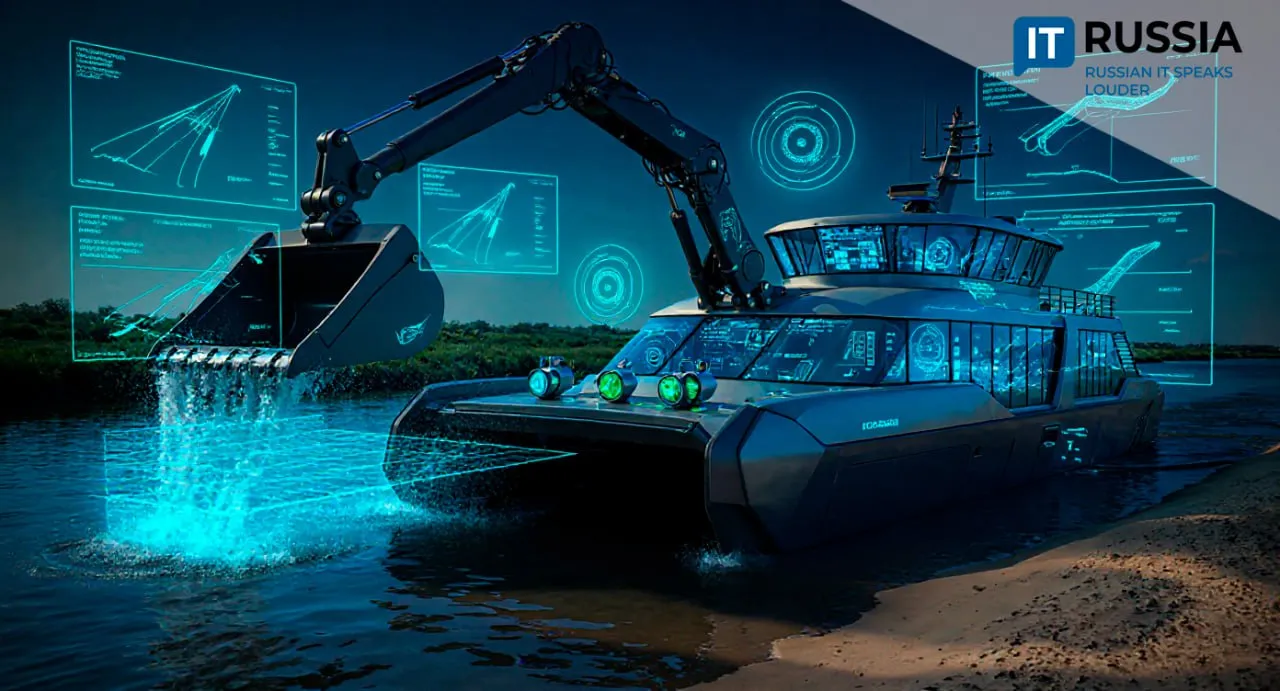

Serial production of amphibious dredgers with artificial intelligence marks a breakthrough in Russia’s hydro-engineering industry.
Smart Amphibian
The Russian company Ural Shipbuilding Plant of Dredgers and Small Technical Fleet Vessels (USZMF, brand “Verfer”) has taken a major step forward in domestic mechanical engineering by launching the development and serial production of innovative amphibious dredgers.
The uniqueness of the project lies in its combination of amphibious mobility, high autonomy, and integration with AI—giving the new machines a clear edge over foreign analogues.
The design incorporates advanced engineering solutions. The self-propelled amphibious dredger can operate both in depths of up to six meters and in shallow waters. Its modular system allows for quick equipment swaps—from an excavator bucket to a slurry pump with a milling cutter.
A key feature is proprietary software developed by Verfer specialists. Using AI algorithms, it boosts operational efficiency by 20% and runs on the company’s own hardware platform. A 3D positioning system displays the underwater topography in real time, marking processed areas.
Importantly, Verfer has completely eliminated foreign components from this critical segment of hydro-engineering equipment.
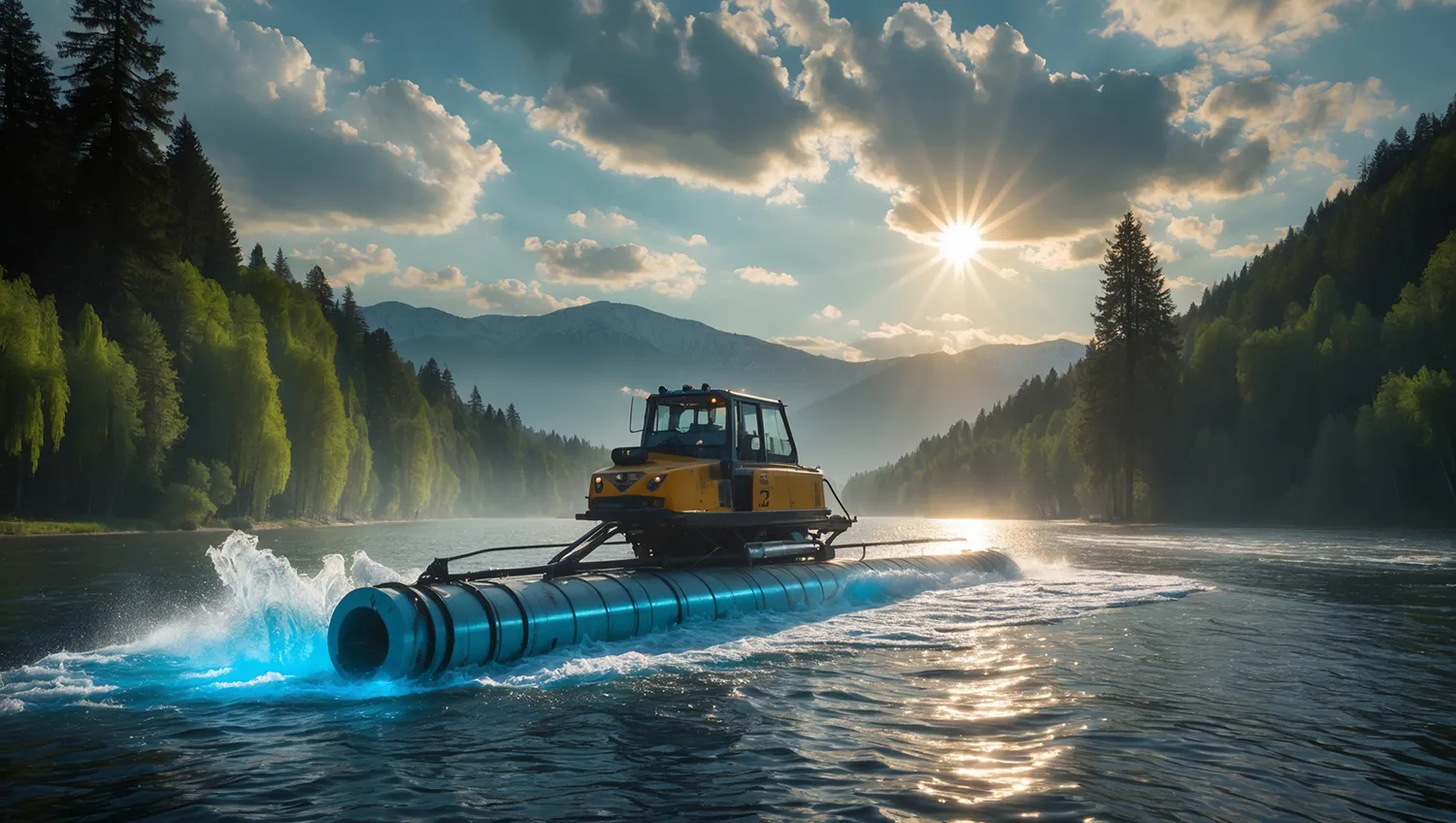

Comprehensive Waterbody Maintenance
These self-propelled amphibious machines are designed for comprehensive waterbody maintenance—from cleaning silt and debris from the bottom to deepening riverbeds and extracting minerals. Initial tests of the “smart” amphibian in the summer of 2025 demonstrated high efficiency and reliability.
The machine excelled in areas with complex underwater terrain, high soil viscosity, and variable depths—conditions where traditional equipment often struggles. Thanks to AI, the dredger can independently assess bottom conditions, choose optimal operating modes, and adapt to changing environments without operator intervention.
Advancing Domestic IT Solutions in Hydro-Engineering
Verfer has already started serial production, aiming to produce three units by the end of 2025 and expand output to 12 amphibians in 2026—a scale-up that reflects strong domestic demand.
The launch of serial production is strategically important not only for the region but for the entire country. Advancing hydro-engineering solutions contributes to Russia’s technological sovereignty. These machines directly improve environmental conditions by effectively cleaning waterways, preventing river and reservoir silting, and restoring navigable channels without harming ecosystems.

A Powerful Tool for Urgent Tasks
Similar dredgers have already been used to clean the Miass River in Chelyabinsk. The new model offers broader functionality—it can also be deployed in construction and other industries.
For municipal services and environmental agencies, these innovative amphibious dredgers are a powerful tool for urgent needs: mitigating flood damage, deepening coastal areas, and rehabilitating polluted waterbodies. With their amphibious design, they can travel over water and land, including marshes and hard-to-reach areas. The equipment is also fitted with systems for extracting sand and other minerals from the bottom.
In Line with Global Industrial Trends
Russia’s market already features dredgers from various manufacturers, each with unique designs and capabilities. Domestic shipyards like Lotos and Tsymlyansk Ship Mechanical Plant are ramping up production. For example, the 93.159A project series is built entirely with Russian components and will enter service in 2025–2026. New models like the Nikolay Rusanov deliver high performance—up to 7,000 m³/hour.
Automation and digitalization are expanding rapidly. For instance, the Hydromech 4000 Dm dredger is operated by a single person and equipped with thruster-rudder units for enhanced maneuverability.
Hybrid and modular designs are in development, including amphibious dredgers capable of shallow-water operations and autonomous beach landings.
The Russian Ministry of Industry and Trade’s plan through 2027 calls for raising the share of domestic products in shipbuilding to 75%. Russian dredgers are already exported to CIS countries and beyond, with Tsymlyansk models popular abroad for their high productivity.

New Horizons for Technological Modernization
Special attention is being paid to technological advancement. Near-term plans include unmanned and semi-automatic models operated from a central console by one person. This will improve safety and scale up operations—allowing simultaneous control of multiple machines to shorten project timelines and reduce costs.
This strategy aligns with global industrial trends toward automation, digitalization, and energy efficiency.
Path to the International Market
The Russian dredger market is moving toward technological independence and expanded production. By 2026–2027, a fully unmanned amphibian line could launch, with fleets expanding to 12 units or more. Further platform enhancements are expected, including integration with satellite monitoring, real-time data transfer, and AI-based predictive maintenance and route optimization.
Successful testing and positive feedback from early customers pave the way for entry into international markets. The greatest export potential lies in Asia, Africa, and Latin America—regions developing hydro-engineering infrastructure but lacking modern, reliable equipment adapted to local conditions. Russian amphibians, combining durability, mobility, and smart technology, could become a competitive product in these markets.